Friendly Digital Marketing Plan

What is a friendly digital marketing plan?
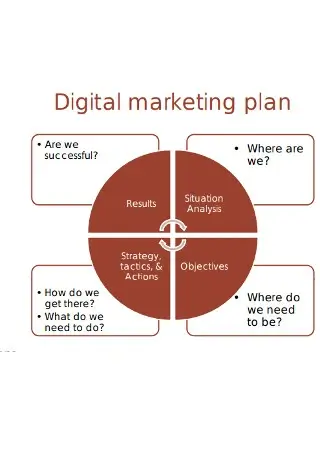
- Opening paragraph — concise context that orients a crawler and a reader
A friendly digital marketing plan is a user-first roadmap that aligns brand goals, audience needs, privacy respect, accessible design, and measurable channels. It balances search visibility, human readability, conversion clarity, and long-term sustainability in one compact strategy.
- How to do the best friendly digital marketing plan step by step?
short overview: Step-driven sequence that converts strategy into repeatable actions.
A step-by-step plan begins with audience definition, moves to keyword and intent mapping, defines content types and UX templates, selects channels with measurable KPIs, implements privacy and accessibility checks, and sets an iterative testing cadence. Each step includes a single owner, a deadline, and a clear success metric. - What to Include in friendly digital marketing plan websites ??
short overview: Concrete site-level components that support friendly marketing.
Include clear value propositions, accessible navigation, semantic HTML, structured data, fast-loading assets, consented tracking, landing-page templates, conversion-focused forms, conversational microcopy, internal linking hub, and an analytics schema that tracks intent-to-action flows. - What are Effective friendly digital marketing plan website growth?
short overview: Growth drivers that scale a friendly site without harming UX.
Effective growth uses content hubization, retention funnels, progressive personalization, referral loops, technical SEO hygiene, and performance budgets. Growth focuses on preserving site speed, trust signals, and consistent user journeys as traffic rises. - What is the Search intent or purpose?
short overview: Intent categories that guide content selection and format.
Search intent maps to informational, navigational, transactional, and commercial-investigational purposes. Matching content format (how-to, hub pages, product pages, comparison guides) to intent increases relevance and lowers bounce friction. - What are the Key elements of a mistake?
short overview: Core error types that sabotage friendly plans.
Key mistakes include ignoring privacy, overtracking, bloated scripts, unclear CTAs, poor mobile UX, keyword-stuffed copy, broken funnels, and missing accessibility semantics. Each mistake reduces trust, raises churn, or wastes ad spend. - What are the Focus words and phrases?
short overview: Intent-aligned phrases that guide on-page language.
Focus words include action verbs tied to intent (compare, buy, learn, download), user-centered nouns (benefit, outcome, proof), and locality or niche modifiers. Use precise, low-ambiguity terms that reflect user queries and micro-conversions. - What are the internal links and anchor texts?
short overview: Internal linking that signals topic structure and distributes authority.
Internal links connect primary hubs to supporting pages using descriptive, intent-rich anchor text. Anchors describe destination purpose, avoid generic labels, and form a shallow, crawlable hierarchy that improves discoverability and session depth. - What are the External links?
short overview: Outbound links that add credibility and context.
External links cite authoritative sources, complementary tools, or standards pages. Use real attributes (noopener, noreferrer, sponsored when applicable) and limit external scripts that degrade performance or privacy. - What are the friendly digital marketing plan website types??
short overview: Common site archetypes for friendly strategies.
Types include lead-generation microsites, resource hubs, product catalogs, community portals, knowledge bases, and hybrid blog–service sites. Each type requires tailored templates for conversions, search intent, and governance. - What are the friendly digital marketing plan websites outline?
short overview: A repeatable page and site skeleton that supports friendly marketing.
Outline: homepage (value + paths), topic hubs (pillar + clusters), landing templates (one CTA), resource pages (downloadable assets), about/trust pages, legal/privacy center, blog stream, and a gated demo or contact funnel. - What are the FAQs?
short overview: Structured Q&A that answers common intent and reduces friction.
FAQs address pricing, timelines, data usage, accessibility standards, deliverables, and support channels. Format questions as short queries and answers as compact, scannable bullets with schema markup for visibility. - What are the guest post mistakes to avoid trust?
short overview: Outreach errors that harm authority and ranking.
Avoid irrelevant sites, low-quality content swaps, over-optimized anchor text, missing attribution, ignoring editorial standards, and failing to disclose sponsored links. Prioritize relevance, editorial value, and transparent linking. - How to Calculate the Estimated Word Count?
short overview: A data-informed method to set content length targets.
Calculate target counts by analyzing top-ranking pages for intent depth, extracting median lengths per intent, adding buffers for examples and visuals, and capping by readability goals. Use the result as a soft target, not a rigid rule. - What are the Target Keywords?
short overview: Primary queries that anchor visibility and conversions.
Target keywords include head terms that define the brand, mid-tail phrases for category traffic, and long-tail queries that signal conversion intent. Assign one primary keyword per page and secondary keywords as semantic support. - 1. How to Research the Primary Keyword?
short overview: Method to validate a primary query’s viability.
Research by measuring search volume, click potential, SERP features, competitor intent, and keyword difficulty. Confirm user intent alignment and map the keyword to a single page objective. - 2. How to Identify Relevant Secondary Keywords?
short overview: Find supporting phrases that expand topical coverage.
Identify secondary keywords via related searches, question tools, on-page co-occurrence, and user feedback. Use them to create subheadings and FAQs that broaden relevance without diluting focus. - How to Turn Your Content Briefs Into High-Converting Blog Posts?
short overview: Brief-to-post conversion checklist for writers.
Provide audience persona, target keyword, search intent, conversion goal, suggested outline, internal links, required data points, tone, and CTA. Include desired word count and sample opening lines to speed quality output. - What is the Title Tag ?
short overview: Title tags that balance clarity, keywords, and click appeal.
Title tags use the primary keyword near the front, include a concise value phrase, and avoid stuffing. Keep length under search display limits and ensure uniqueness across the site. - What is the Meta Description ?
short overview: Meta descriptions that clarify intent and improve CTR.
Meta descriptions summarize the page purpose, mention user benefit, and include a CTA or next step. Keep them concise, unique, and aligned to on-page intent for better click-through performance. - What is the Article Outline?
short overview: A practical structure that supports skimmability and depth.
An outline starts with an intent-aligned intro, followed by pillars, supporting points, examples, visuals, an action-oriented conclusion, and internal links. Each section has one clear purpose and a single micro-CTA. - What are the Headings?
short overview: Hierarchical headings that aid readers and crawlers.
Headings use keywords sparingly, describe section purpose, and follow a logical H1→→ cascade. Keep headings short and parallel in structure to improve scan-ability. - What are the Voice and Tone Guides?
short overview: Rules that enforce consistent brand language.
Voice is concise and human; tone adjusts by audience segment—formal for enterprise, approachable for SMB. Create examples for headlines, CTAs, and error messages to ensure consistent execution. - how to Shaping the content according to the target audience
short overview: Tailor content layers to personal needs and literacy.
Segment by knowledge level and job role, then adjust depth, examples, and terminology. Use modular content blocks so the same asset serves beginners and advanced users through progressive disclosure. - how to Defining and refining your content strategy
short overview: A cycle of planning, publishing, measuring, and pruning.
Define strategy by audience, goals, channels, and success KPIs. Refine by testing headlines, formats, and CTAs using engagement metrics and conversion lifts. Prune low-performing pages regularly. - Tips for Producing a Great Copywriting Brief
short overview: Essentials that make briefs actionable and precise.
Include audience, purpose, primary message, desired structure, examples of tone, mandatory links, keywords, and a clear deadline. Keep the brief one page and include SVG or visual references when layout matters. - 1. Look For Ways to Stand Out From the Competition?
short overview: Differentiators that create unique value signals.
Stand out by offering original data, proprietary templates, unique case studies, or a fresh POV. Emphasize formats competitors lack, such as interactive tools or serialized research. - 2. Provide Context for the Writer Where Necessary?
short overview: Context that accelerates quality and reduces rewrites.
Provide user pain points, competitive gaps, previous content links, and acceptable sources. Include how the piece ties into funnel stages and which KPI it supports. - 3. Include Internal Links With Descriptive Anchor Text?
short overview: Internal links that guide users deeper and transfer topical relevance.
Link from the briefed page to specific resource pages using anchors that describe the linked content. Note preferred landing pages and any nofollow or sponsored attributes. - How to Create Self-Sustainable B2B Content?
short overview: Evergreen systems that reduce manual upkeep.
Build reusable templates, modular assets, a content calendar tied to product cycles, and a governance process for updates. Empower subject-matter owners and automate performance alerts for aging content. - How to Choose a Content Hub: 6 Types and Examples?
short overview: Hub archetypes matched to goals and resources.
Hub types: resource library, learning academy, tool center, trend lab, case-study vault, and newsroom. Choose the hub that aligns to audience learning patterns and internal content capacity. - How Content Readability Affects SEO and Rankings?
short overview: Readability reduces friction and improves engagement signals.
Readability raises time on page, lowers pogo-sticking, and increases share rates. Use short sentences, active voice, clear subheads, and visual breaks to help both humans and algorithms interpret value. - What is the Privacy Preference Center?
short overview: Central control point for user data choices.
A privacy preference center lists tracking categories, purposes, allowed vendors, and granular toggles. It stores user consent choices, offers easy withdrawal, and exposes a machine-readable consent signal to compliant analytics. - Why Our Social Media Service Website Stands Out:?
short overview: Differentiators framed for trust and utility.
The site emphasizes transparent scheduling policies, privacy-safe engagement analytics, content templates for platform variance, and documented community guidelines that protect brand reputation. - How are friendly digital marketing plan websites Used?
short overview: Common user journeys and business uses.
Sites serve discovery, evaluation, and conversion flows: discovery via search and social, evaluation via case studies and comparisons, conversion via streamlined contact forms and proof elements. Each use aligns to mapped KPIs. - Who Are You Writing This For?
short overview: Audience definition that guides tone and depth.
Define target as buyer persona(s) with role, responsibility, purchase power, and preferred content formats. Document primary objections and the micro-CTAs that resolve each objection. - What Is Your Goal for Creating Content?
short overview: Single, measurable objective per piece avoids mixed signals.
Goals include lead generation, organic traffic growth, retention, or authority building. Assign a leading metric (e.g., MQLs, sessions, time on page) and instrument it before launch. - What Action Do You Want Users to Take?
short overview: One primary action per page sharpens UX and copy.
Choose a single primary CTA—download, request demo, subscribe, book call—and support it with micro-CTAs that reduce friction. Make the path from intent to action visible within two scrolls. - What is SEO Research?
short overview: Systematic discovery of queries, competitors, and opportunity gaps.
SEO research captures intent patterns, content gaps, technical blockers, and SERP features. Combine query lists, competitor outlines, and a prioritized roadmap for content and technical fixes. - User Intent and SERP Analysis
short overview: Examine actual search results to infer user needs.
Analyze top-ranking pages, featured snippets, People Also Ask, and ad presence to deduce intent. Match page type and depth to what users encounter and reward. - What is the importance of a friendly digital marketing plan?
short overview: Why friendly approaches produce durable returns.
Friendly plans increase trust, reduce churn, and lower acquisition costs by emphasizing privacy, accessibility, clarity, and relevant content. They create compounding value as users convert and return. - What is marketing optimization?
short overview: Iterative improvements to campaign efficiency and outcomes.
Marketing optimization refines targeting, creative, placement, and timing using conversion data. It reduces wasted spend and increases per-channel ROI through systematic tests. - What is digital optimization?
short overview: Site and campaign tweaks that improve digital performance.
Digital optimization includes performance budgets, image compression, script auditing, A/B testing, and funnel simplification to improve speed and conversions. - What are sales and marketing optimization?
short overview: Alignment of revenue functions to shorten time-to-revenue.
Sales and marketing optimization synchronizes lead definitions, routing rules, content stages, and feedback loops. The result is faster qualification and higher lead-to-deal conversion. - What is brand optimization?
short overview: Actions that improve brand clarity and recall.
Brand optimization focuses on consistent messaging, memorable assets, a compact value ladder, and reputation management across channels to increase trust and preference. - What are digital-marketing optimization tools?
short overview: Tool categories that enable measurement and automation.
Tool categories include analytics, tag management, A/B testing, performance monitoring, content workflow, and privacy consent orchestration. Choose tools that minimize page bloat and centralize data governance. - What is personalized marketing campaign optimization?
short overview: Personalization that increases relevance without invading privacy.
Optimization uses first-party signals, session-level intent, and progressive profiling to tailor content. Respect consent and expose preference controls so personalization remains user-centered. - What is marketing performance optimization?
short overview: Measurement-driven improvements across channels.
Performance optimization sets channel-level KPIs, attributes conversions sensibly, and reallocates budget to paths with better unit economics. Use cohort analysis to avoid following short-term noise. - what is marketplace optimization
short overview: Tactics to improve discoverability inside third-party marketplaces.
Marketplace optimization includes title clarity, enriched descriptions, optimized images, localized pricing, review volume, and conversion-focused attributes to surface product listings. - What are the best wordpress extensions?
short overview: Extension categories that keep sites friendly and fast.
Recommended extension types include caching, image optimization, SEO schema, accessibility helpers, consent managers, and lightweight page builders. Prioritize extensions with clean code and active maintenance. - What are optimizations defined?
short overview: Definition that frames optimization as purposeful refinement.
Optimizing is the act of improving a metric by changing inputs, measuring the effect, and repeating. It emphasizes causality, not hacks, and treats speed, relevance, and trust as co-equal goals. - What are the most popular wordpress plugins?
short overview: Popular plugin categories that solve common needs without excess.
Popular plugins cover SEO, caching, security, backups, forms, and images. Use only essentials and audit plugin impact on load times and privacy. - What is an internet marketing optimization company?
short overview: Vendor roles and what to expect from an optimization partner.
An optimization company provides analytics audits, conversion-rate experiments, campaign restructuring, and governance frameworks. Select a partner with measurable case studies and transparent reporting. - What is email marketing optimization?
short overview: Tactics that increase deliverability and engagement.
Email optimization focuses on subject lines, sender reputation, segmentation, send cadence, and mobile-friendly templates. Test with small cohorts and scale variants that raise open and click rates. - What is ad optimization?
short overview: Iterating creatives, bids, and placements to reduce cost-per-action.
Ad optimization tests messaging, audience slices, landing pages, and bidding strategies. Use incremental lift tests to distinguish causal impact from correlation. - What is feed optimization?
short overview: Tuning product or content feeds for platform algorithms.
Feed optimization standardizes attributes, improves titles, provides high-quality images, and uses canonical identifiers to increase matching and click-through in shopping and discovery feeds. - What is content marketing optimization?
short overview: Align content to intent, format, and promotion channels for impact.
Content optimization updates headlines, adds structured data, prunes stale sections, and re-promotes high-value pieces. Measure organic traffic, assists, and conversions to prioritize efforts. - What is campaign optimization?
short overview: Holistic tuning across creative, audience, and landing experience.
Campaign optimization synchronizes ad copy, offers clarity, landing UX, and post-click nurture to improve end-to-end conversion rates and lower friction. - what is product optimization
short overview: Improving product-market fit and discoverability.
Product optimization blends pricing experiments, attribute clarity, imagery, and real-user feedback to increase conversions in both owned channels and marketplaces. - Which of these items is not included in marketing optimization?
short overview: Distinguish tasks that are outside optimization scope.
Creative ideation without measurement, pure brand storytelling with no KPI, and unrelated legal compliance tasks are not optimization activities. Optimization requires measurable hypotheses and tracked outcomes. - What is optimized online marketing?
short overview: Characteristics of an optimized online program.
Optimized online marketing is data-instrumented, privacy-compliant, performance-budgeted, mobile-first, and built around clear conversion paths. It minimizes waste and maximizes repeatable customer journeys.



